Posted on November 27, 2025
Growth
Tags:

The Business Model Canvas (BMC) is a tool that helps visualize and plan a business model in a single page. It was developed by Alexander Osterwalder, a business theorist who aimed to simplify the process of designing business models by showing all key components in one connected view—rather than writing hundreds of pages of business plans.

For Entrepreneurs / Startups > BMC helps identify how your business creates value, who you sell to, and where your revenue comes from.
For Employees > BMC isn’t only for business owners. It helps employees understand the big picture and how their work contributes to the organization’s value and goals.
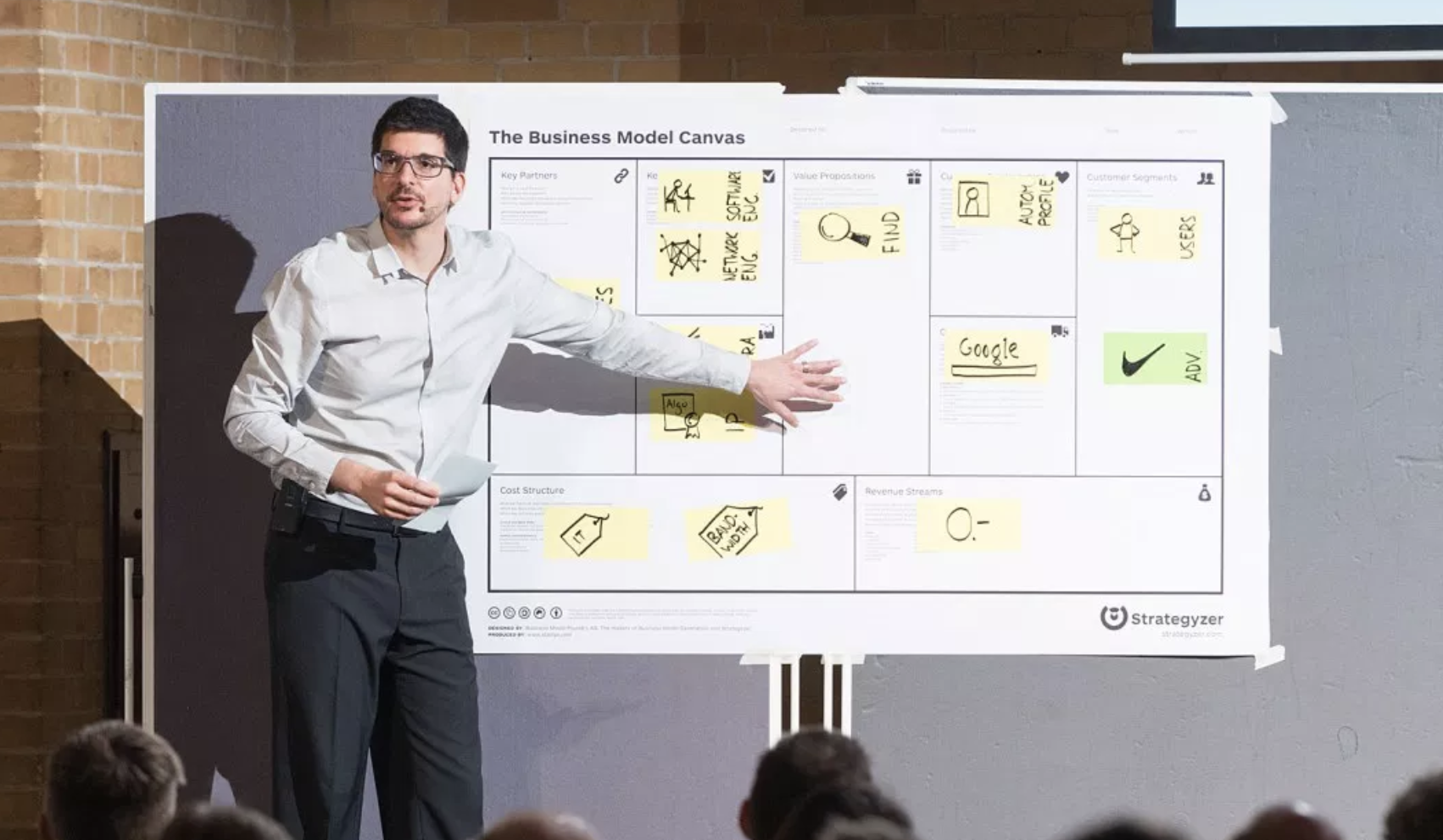
Below are the nine core elements of a BMC and why each is important:
1. Key Partners
Business partners enhance the organization’s capabilities—whether through resources, technology, capital, or distribution channels. For example, an online business needs reliable logistics partners and payment systems to operate smoothly.
2. Key Activities
These are the essential actions required to deliver value to customers, such as product development, service delivery, or innovation. Example: A busy restaurant might develop an online queueing system to improve customer experience.
3. Key Resources
These include everything the business needs to operate successfully:
Physical assets (machinery, office buildings)
Intellectual property (patents, trademarks)
Human resources (team members)
4. Value Proposition
This is the heart of the BMC. You must define:
What makes your product/service unique
What customer pain points you solve
How you stand out from competitors
Example: Food delivery service that promises “delivery within 30 minutes”.
5. Customer Relationships
Ways to build and maintain customer relationships, such as:
Membership or subscription programs
After-sales service and feedback collection
Community building (Facebook groups, LINE OA)
Automated systems (chatbots, self-service tools)
These help strengthen trust and brand loyalty.
6. Customer Segments
You must identify who your customers are.Segmenting by age, gender, income, occupation, behaviors, or special needs helps you communicate and market effectively.
7. Channels
These are the methods used to deliver value to customers. Channels include:
Online (website, e-commerce, social media)
Offline (stores, distributors)
Choosing the right channels depends on your business and customer behavior.
8. Revenue Streams
Your income may come from:
Subscription fees
Direct sales
Rental or per-use fees
Advertising
Understanding revenue streams helps you identify core income sources and expansion opportunities.
9. Cost Structure
Understanding costs helps businesses plan and stay financially healthy.Costs include:
Fixed costs: rent, salaries
Variable costs: raw materials, production labor
ExampleOther expenses: marketing, outsourcing
Seeing the full cost structure helps improve efficiency and reduce unnecessary spending.
Start with Customer Segments and Value Propositions
Use sticky notes for flexibility
Keep everything short, clear, and simple
Update regularly as the market changes
Customer Segments: Local workers and students
Value Proposition: Quality coffee, affordable prices, cozy atmosphere
Channels: Physical shop + food delivery apps
Customer Relationships: Loyalty cards, promotions
Revenue Streams: Coffee and bakery sales
Key Resources: Baristas, coffee ingredients
Key Activities: Coffee brewing, marketing
Key Partners: Coffee bean suppliers, delivery apps
Cost Structure: Rent, salaries, raw materials
Advantages
Clear overview of the entire business on one page
Easy to understand and communicate with teams
Flexible and adjustable
Limitations
High-level overview; lacks deep details
May not cover legal or complex financial issues
Works best when paired with tools like SWOT or full business plans
Canva (free templates)
Miro / MURAL (collaborative online whiteboards)
Strategyzer (official platform by BMC creators)
Helps employees understand the big picture and their impact
Useful for freelancers or anyone starting small projects
Helps analyze your company’s strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities

Final Thoughts
The Business Model Canvas is an essential tool for understanding and designing business strategies. It benefits entrepreneurs, startups, and working professionals by connecting daily work to the organization’s value and long-term goals. If you want to plan a new business or better understand strategic work, BMC is a tool you should not overlook. For more content on career growth, marketing, and skill development, explore Jobcadu, the career platform that inspires your professional journey.